Gentle antiseptic on the skin

Cuts and grazes are part and parcel of life. Knowing how to properly clean and treat basic minor wounds will help prevent a graze or wound becoming infected and aid in proper healing.
A cut is essentially a tear to the skin. A cut can be described as a laceration, which is caused by a blunt force like a fall, or an incised wound, which is caused by a sharp object like a knife or piece of glass slicing into the skin. A bite injury can also be considered a type of cut.
For minor cuts, the first thing you may need to do is stop the bleeding. Remove any clothing that’s in the way, then apply firm but gentle pressure with a clean cloth, gauze or bandage. If it’s possible, try to raise the cut above heart level.
Once the bleeding has stopped, clean the wound to help remove any germs and foreign objects. Start by flushing it out with warm, clean tap water or an antiseptic liquid. You can use soap and a soft washcloth to clean the skin around the cut but try to keep the soap out of the wound itself.
After cleaning the cut, cover it with a clean dressing. This will help to keep the wound clean and protect the area as it heals. Keeping the wound covered also keeps the wound moist, which can aid healing.
If your cut is deep or if you can’t stop the bleeding, apply appropriate first aid and seek medical attention immediately. You may need to have the wound closed with stitches, glue or staples.
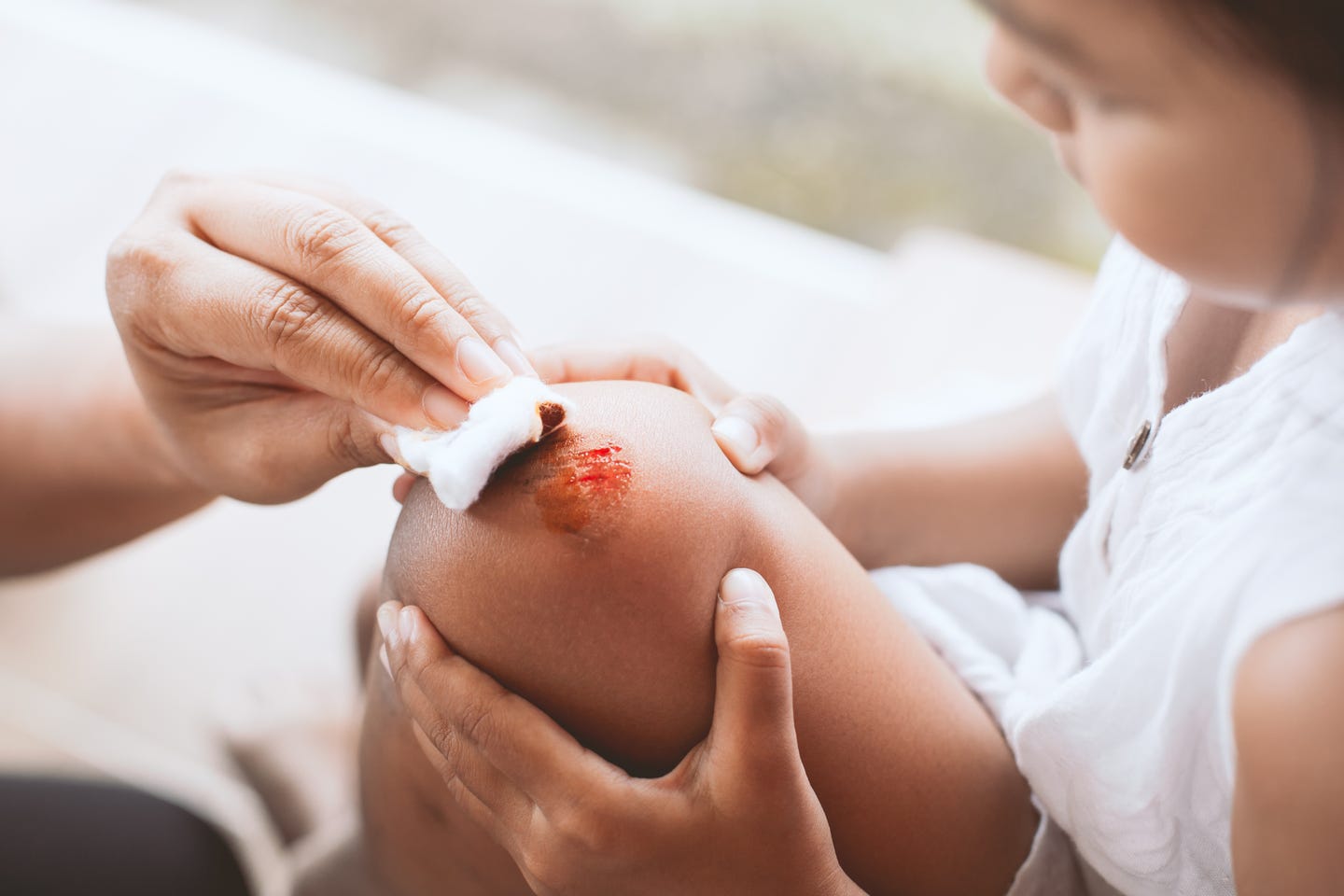
A skin graze or abrasion is when the surface layers of the skin have been scraped and broken, usually by friction against a rough surface. Thin-skinned bony areas like the knees and elbows are more prone to grazes.
Just like a cut, cleaning the graze is important to remove any dirt and other foreign objects. Use clean water and a piece of sterile gauze (or other non-shedding cloth) to gently wipe the graze – don’t scrub at embedded dirt as this can traumatise the wound more. After 5 minutes, rinse the graze with flowing tap water, then cover with an appropriate non-stick sterile dressing.
For grazes where deep layers of skin have been removed, apply appropriate first aid and seek urgent medical attention.
Our skin provides a natural barrier to germs. When we get a wound, that barrier is broken, and harmful bacteria are able to enter and may cause infection. Bacteria can be introduced by whatever it is that punctured the skin, or even by the movement of bacteria that otherwise live harmlessly on our skin.
An infection disrupts the healing process and can make you very sick. Signs of an infected wound include:
To help reduce the risk of an infected wound, you can:
Aside from when you are experiencing signs of infection like those mentioned above, you should also see a doctor if:
Using Dettol Antiseptic Liquid to clean cuts or scratches can help protect the wound from infection. Make sure to dilute the Dettol first by mixing 20ml with 400ml of water. This diluted mixture can then be used to cleanse the wound.
For a more convenient option, Dettol Antiseptic Wound Wash Spray comes ready to use, and the spray format also means you can avoid touching the wound. Simply spray to wash away any dirt or debris, then wipe up any excess liquid with cotton wool or tissue.
A few important things to remember when using Dettol:
When you get a wound, your body will start to repair itself immediately. First, the body will form a blood clot at the injury site and send white blood cells to start cleaning it of bacteria and other foreign objects. Then, new layers of skin will start to grow around the wound, encouraging the edges of the wound to contract and close. Over time, more and more new skin cells will be added to cover the wound.
There are a few things you can do to help your body along with this process:
Whatever the minor mishap, the important thing to remember is to properly clean and dress any cuts or grazes. By including Dettol in your first aid routine, you can help protect against infection.
Always read the label. Follow the directions for use. If symptoms persist, talk to your health professional.
First published: 15th February 2021
Last updated: 30th November 2023